Resume Classification Using NLP
Project Overview:
This project involves the implementation of both statistical and modern deep learning models to classify resumes. Utilizing Decision Trees, Random Forests, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, alongside word embeddings with Word2Vec, the project aims to accurately categorize resumes into predefined job roles. By comparing the performance of these diverse models, the project demonstrates the strengths and applicability of each approach in the context of natural language processing and resume classification.
Objectives
- Compare Classification Approaches:
- Statistical Models: Utilize models like Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, and Random Forest with feature extraction techniques such as Bag of Words and TF-IDF.
- Embedding-Based Models: Explore deep learning models like CNN and LSTM with Word2Vec embeddings.
- Assess Model Performance:
- Use metrics such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-Score to compare models.
- Identify strengths and limitations of each approach based on dataset size and complexity.
- Contribute to Recruitment Efficiency:
- Demonstrate scalable and accurate resume classification for large datasets.
- Highlight practical NLP applications in recruitment, focusing on reduced bias, improved accuracy, and time savings.
Implementation
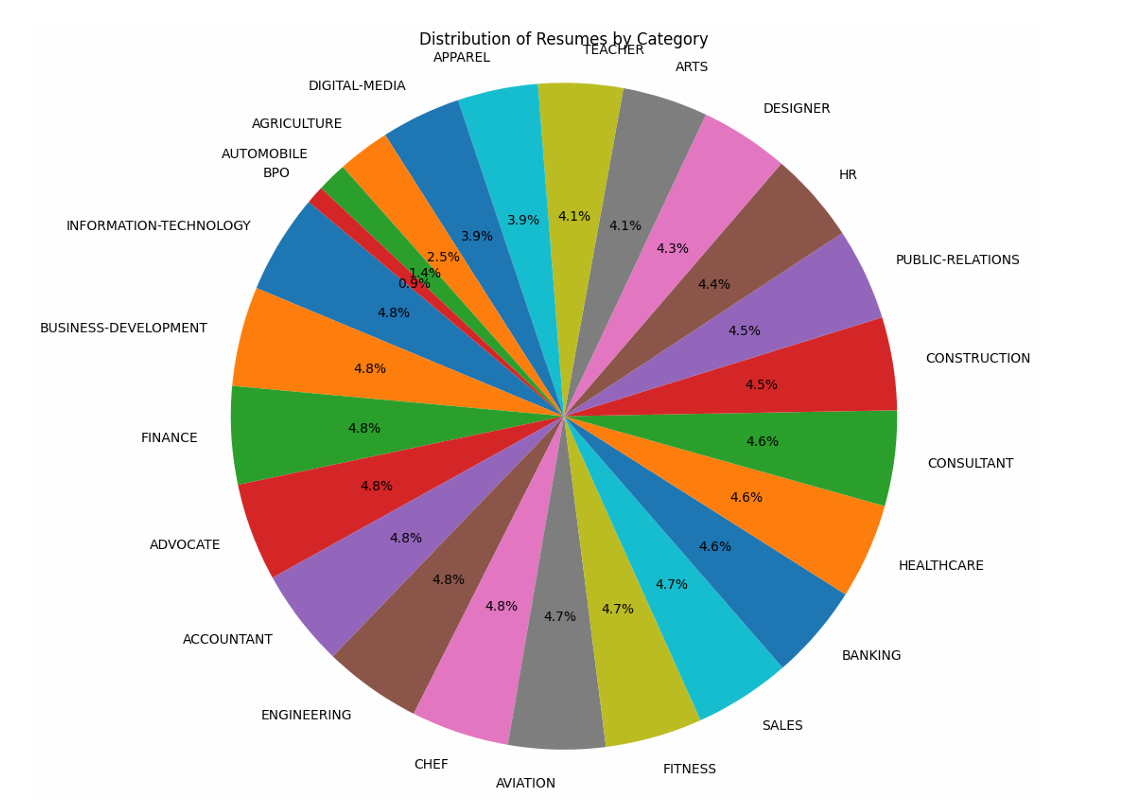
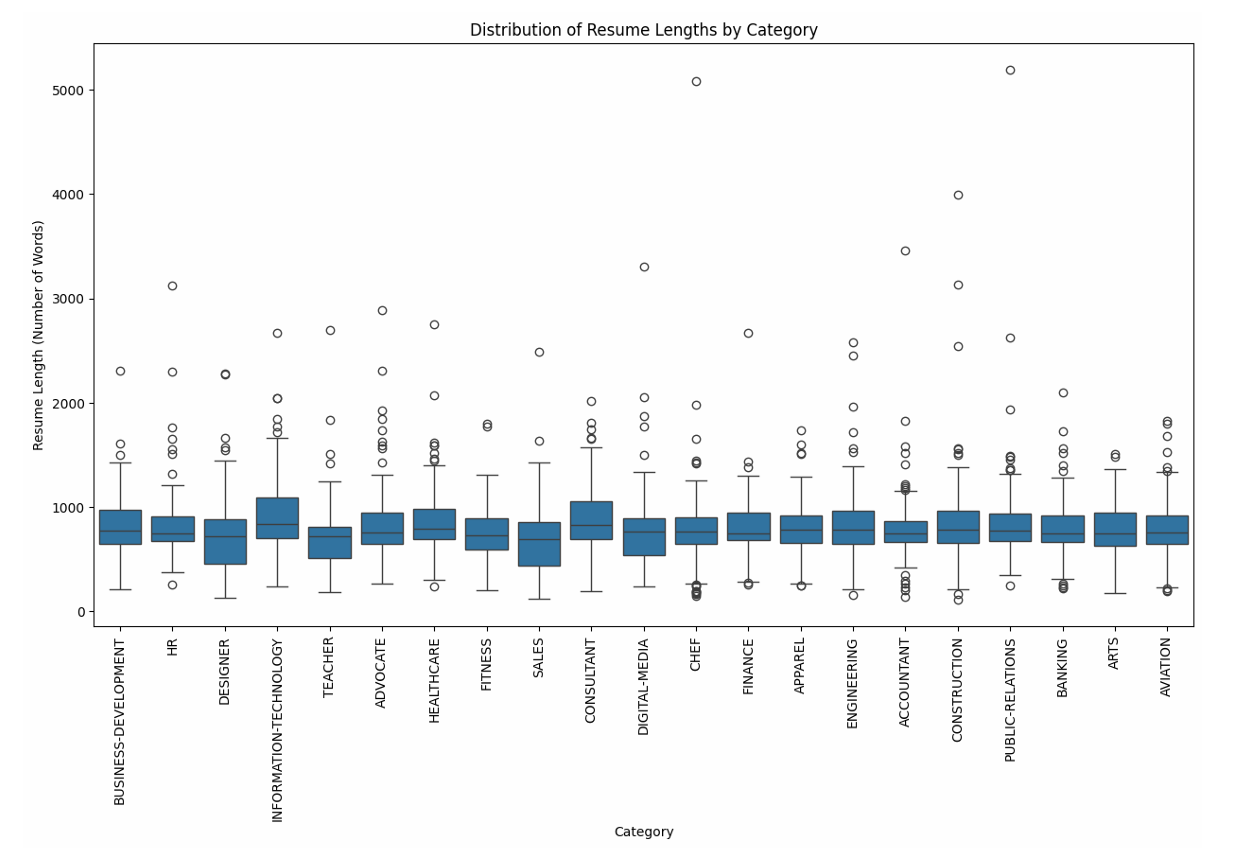
1. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Analyze the dataset to understand its structure, distribution of job categories, and the nature of textual data in resumes.
2. Data Preprocessing
- Text Preprocessing: Remove stop words, tokenize, lemmatize, and clean data to standardize inputs.
- Label Encoding: Encode job categories as numerical labels for classification.
3. Baseline Statistical Model
- Implement a Bag of Words model with a Naive Bayes classifier for initial performance benchmarking.
4. Traditional Statistical Models
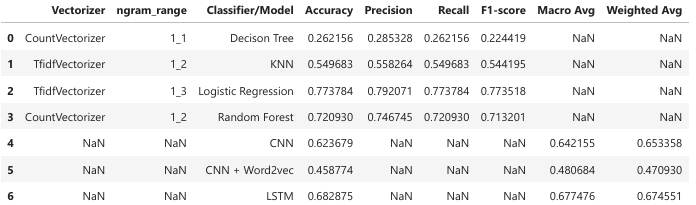
- Feature Extraction: TF-IDF Vectorizer with n-gram ranges (e.g., unigram, bigram, trigram).
- Classifiers: Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Decision Tree, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN).
5. Embedding-Based Models
- Prepare embeddings using Word2Vec to convert text data into dense vector representations.
- Deep Learning Models:
- CNN: Extract local features with convolutional layers.
- LSTM: Capture sequential dependencies in the text.
Performance Insights
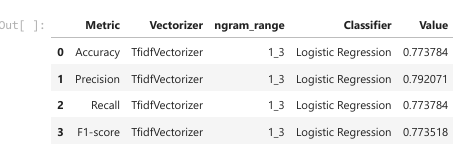
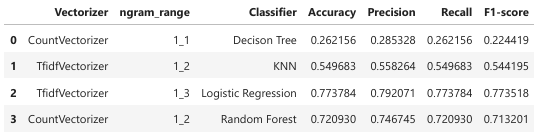
- Statistical Models:
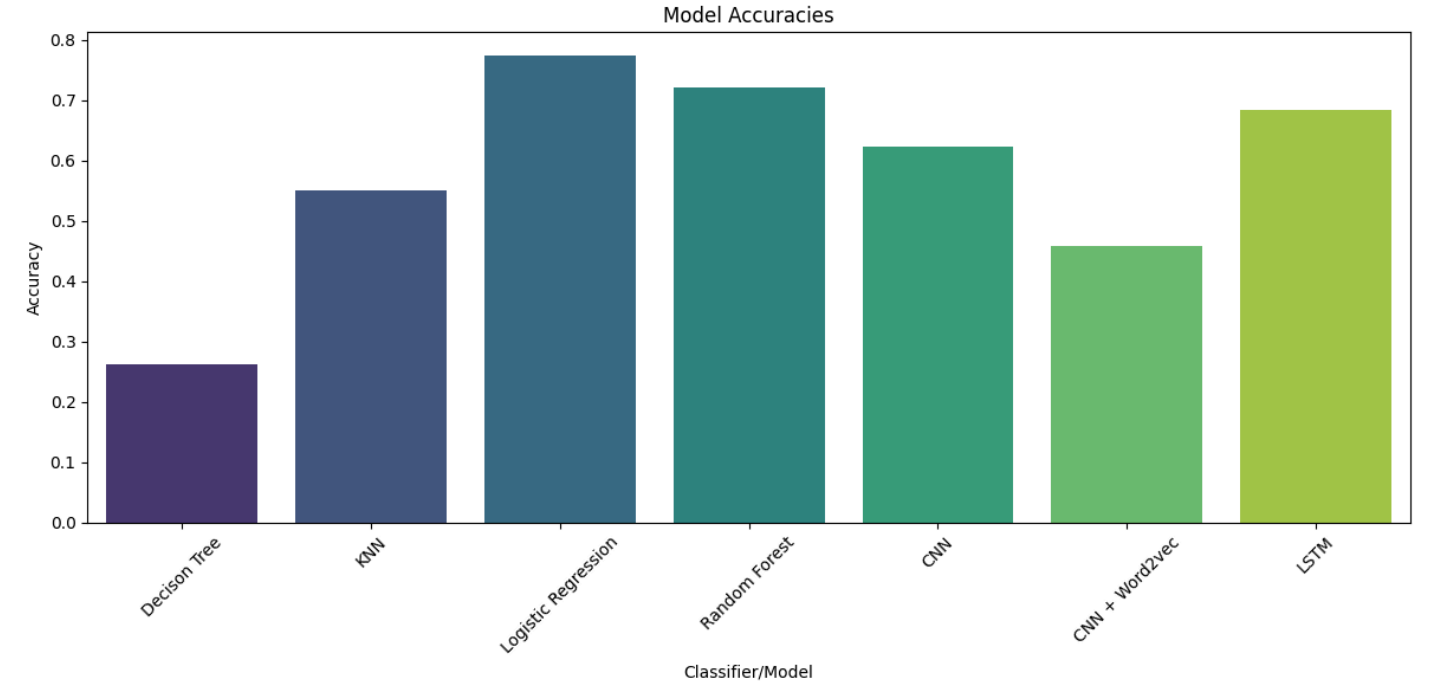
- Logistic Regression with TF-IDF Vectorizer (n-gram range: 1–3) outperformed other statistical models, achieving:
- Decision Trees exhibited the lowest performance due to overfitting tendencies and inability to capture text patterns.
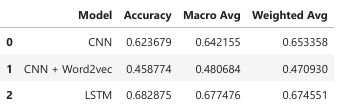
- Embedding-Based Models:
- LSTM outperformed CNN, achieving an accuracy of 0.682875, demonstrating its strength in handling sequential data.
- CNN with Word2Vec underperformed (accuracy: 0.458774), likely due to misaligned embeddings or insufficient parameter tuning.
Key Findings
Model Suitability
- Statistical Models:
- Practical for small datasets due to simpler implementation and lower computational requirements.
- Logistic Regression and Random Forest are particularly effective with feature engineering techniques like TF-IDF.
- Embedding-Based Models:
- More suitable for larger datasets where capturing contextual nuances is critical.
- Require significant data, embedding quality, and careful hyperparameter tuning.
Comparative Advantages
- Statistical Models: Quick to implement, efficient for straightforward tasks, and computationally inexpensive.
- Embedding-Based Models: Better at capturing semantic meanings and patterns in complex datasets.
Contributions
- Improved Recruitment Processes:
- Automating resume classification enhances accuracy and reduces bias in initial screening stages.
- Scalable Solutions:
- Demonstrates scalability for processing large datasets in recruitment and beyond.
- NLP Advancements:
- Offers a framework for organizations to adopt similar technologies for real-world applications.